Impingement/Bursitis/Tendonitis
What is Bursitis?
Bursitis is inflammation of a bursa and tendonitis is inflammation of a tendon. A bursa is a fluid filled sac that sits between muscles or tissues to cushion and reduce friction. In the shoulder there is a rather large bursa between the deltoid muscle and joint. This is called the sub-deltoid bursa. This bursa can often become inflamed due to abnormal joint movements, poor posture and weakness of the surrounding musculature. This causes strain to the tissues and excessive friction on the bursa. People tend to feel pain with movement and especially movement out to the side or reaching behind them.
What is Tendonitis?
Tendonitis is an inflammation of the shoulder tendons. Tendons connect muscles to bones. In the shoulder common areas for tendonitis are in the rotator cuff tendons (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor and subscapularis) and bicep tendons. The signs of inflammation are pain, warmth, redness, tenderness to touch, and loss of function. Shoulder tendonitis (often called Rotator Cuff Tendonitis) can occur when the rotator cuff is overloaded, fatigued, traumatized, and with age-related degenerative changes. Pain can be felt deep in the shoulder or in the front of the shoulder. Pain is usually felt as a sharp, catching sensation with certain movements.
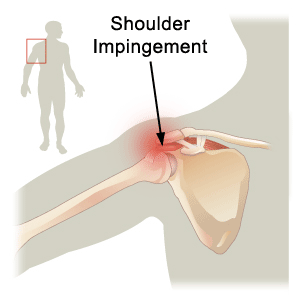
What is Impingement?
Impingement syndrome is a common shoulder condition seen in active adults, especially as they get older. This condition is closely related to shoulder bursitis and rotator cuff tendinitis. These conditions may occur alone or in combination.
Pinching or impingement of the rotator cuff tendons occurs in a region under a bony structure called the acromion (the projection of the shoulder blade that forms the tip of the shoulder). Impingement happens when the arm is raised overhead repeatedly, or raised overhead with a heavy load in your hand, or may occur when you sleep on your shoulder. X-rays may show a hook or spur that increases the odds that you will pinch the rotator cuff tendons.
How physical therapy helps
Physical therapy is the first line of conservative treatment for bursitis and tendonitis. Since most bursitis and tendonitis is due to underlying abnormal mechanics of movement and weakness, our trained physical therapists evaluate your movement to pinpoint the exact source of the trouble. Modalities may be used to alleviate pain and discomfort, while hands-on therapy improves joint mechanics and movement.
Treatment for impingement or rotator cuff tendonitis usually involves rest, anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen, physical therapy to restore proper strength and movement, and less often, a cortisone injection.
Finally, gentle strengthening exercises and joint coordination exercises help to restore stability to the affected area and to prevent re–occurrence of the symptoms.
Hours of Operation
Monday 7:00 - 5:00
Tuesday 7:00 - 12:00
Wednesday By Appointment Only
Thursday 7:00 - 5:00
Friday 7:00 - 12:00
Contact Us Today
570-726-0331
Allow us to help you "Achieve Your Goals"! Give us a call today to schedule an appointment!
Contact Info
© 2019 Chappell Physical Therapy. All rights reserved | Marketing by Mid-Atlantic Marketing Group