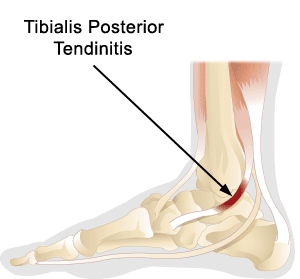
Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
The posterior tibial tendon is one of the most important tendons of the leg. A tendon attaches muscles to bones, and the posterior tibial tendon attaches the calf muscle to the bones on the inside of the foot. The main function of the tendon is to hold up the arch and support the foot when walking. Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed or torn. As a result, the tendon may not be able to provide stability and support for the arch of the foot, resulting in flatfoot.
An acute injury, such as from a fall, can tear the posterior tibial tendon or cause it to become inflamed. The tendon can also tear due to overuse. For example, people who do high-impact sports, such as basketball, tennis, or soccer, may have tears of the tendon from repetitive use. Once the tendon becomes inflamed or torn, the arch will slowly fall (collapse) over time.
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is more common in women and in people older than 40 years of age. Additional risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and hypertension.
Symptoms include pain along the inside of the foot and ankle, where the tendon lies. This may or may not be associated with swelling in the area. Pain is generally worse with activity. High-intensity or high-impact activities, such as running, can be very difficult. Some patients can have trouble walking or standing for a long time.
Most patients can be treated without surgery, using orthotics and braces. If orthotics and braces do not provide relief, surgery can be an effective way to help with the pain. Surgery might be as simple as removing the inflamed tissue or repairing a simple tear. However, more often than not, surgery is very involved, and many patients will notice some limitation in activity after surgery.
How physical therapy helps
Physical therapy is very beneficial in treating posterior tibial tendonitis. At first, we evaluate your movement, posture, walking pattern, ankle and foot mobility. Our gentle hands-on therapy is great for soothing the irritated tissue in the foot and also improving range of motion in the foot and ankle joints.
Modalities, such as ultrasound and ice may be used to reduce swelling and pain quickly. Our goal is to reduce your pain quickly and strengthen your feet for long-term results.
If surgery is needed for your recovery, rest assured that you are in the right hands for your rehabilitation. We work closely with your physician's rehabilitation protocols. The priority is to manage your pain and swelling after surgery, gradually increasing your range of motion in the knee per your post-surgery protocol. Rehabilitation may require six to twelve months of progressive care.
As time progresses, we work with you to gain your strength back in the ankle, improve stability of the joint, get you back to walking normally and eventually back into advanced movements including running.
Hours of Operation
Monday 7:00 - 5:00
Tuesday 7:00 - 12:00
Wednesday By Appointment Only
Thursday 7:00 - 5:00
Friday 7:00 - 12:00
Contact Us Today
570-726-0331
Allow us to help you "Achieve Your Goals"! Give us a call today to schedule an appointment!
Contact Info
© 2019 Chappell Physical Therapy. All rights reserved | Marketing by Mid-Atlantic Marketing Group